Wonderful Tips About Why Is 3 Phase Cheaper To Run

If A 1Phase Supply Is 230V, Why 3Phase 400V & Not 690V?
Understanding the 3-Phase Advantage
1. Powering Your World Efficiently
Ever wondered why big industries and commercial buildings often rely on something called "3-phase" power? It's not just a fancy electrical term; it's often a money-saver in the long run. The core principle behind this cost-effectiveness lies in how 3-phase systems deliver power more consistently and efficiently compared to their single-phase counterparts. Think of it like this: instead of one strong push, you get three synchronized pushes that keep the motor spinning smoothly.
Consider an analogy: Imagine pushing a merry-go-round. If you push only at one point (single-phase), it requires quite a bit of force to get it started and keep it moving, with moments of slowing down between pushes. Now, picture three people pushing at different points simultaneously (3-phase). The merry-go-round spins much more smoothly and requires less effort from each person to maintain its speed. That's essentially what 3-phase power does — it provides a more constant and balanced power flow.
One of the main reasons 3-phase is cheaper to run stems from its superior efficiency. Single-phase motors require extra components, such as capacitors, to start and run, leading to energy losses. 3-phase motors, on the other hand, inherently have higher starting torque and run more efficiently without needing these extras. This increased efficiency translates into lower electricity bills over time, especially for large motors that run continuously.
Furthermore, the reduced stress on the electrical grid is another critical factor. Because 3-phase power distributes the electrical load more evenly, it helps prevent voltage drops and imbalances. This ultimately leads to a longer lifespan for electrical equipment and reduced maintenance costs. It's like having a well-balanced diet for your electrical system, ensuring everything runs smoothly and avoids premature wear and tear.
The Motor Story
2. How 3-Phase Motors Outperform
Let's delve deeper into the mechanics of motors. Single-phase motors tend to be less efficient, meaning they convert less electrical energy into mechanical work. A portion of the energy is lost as heat due to the extra components required for operation. These inefficiencies add up over time, leading to higher energy bills. Think of it as driving a car with a leaky gas tank — you're burning more fuel to go the same distance.
3-phase motors, conversely, boast a simpler and more robust design. They don't need the extra starting components, and their inherent design provides a smoother, more efficient power delivery. This not only saves energy but also reduces the risk of motor burnout and costly repairs. They're like the energy-efficient hybrids of the motor world, optimizing performance and minimizing waste.
The longevity of 3-phase motors is another significant advantage. The balanced power distribution reduces stress on the motor windings and bearings, leading to a longer lifespan. This means less frequent replacements and fewer unexpected breakdowns. Businesses that rely on heavy machinery can save a considerable amount of money on maintenance and downtime over the years.
Beyond pure efficiency, the power-to-size ratio is also impressive. A 3-phase motor can deliver more power than a single-phase motor of the same size. This is crucial in applications where space is limited, such as manufacturing plants and industrial facilities. It's like getting a bigger engine in a smaller car — more power without sacrificing space.

Introduction To Power Inverters What Is 3Phase Power?, Part 6 Video
Reduced Infrastructure Costs and Load Balancing
3. Power Distribution Made Smarter
While the initial installation of a 3-phase system might be slightly more expensive due to the need for specialized equipment, the long-term operational savings often outweigh these upfront costs. Consider the reduced wiring requirements. 3-phase systems can transmit the same amount of power with smaller conductors, leading to savings on copper and installation labor.
The ability to balance electrical loads is another key benefit. In a single-phase system, uneven distribution of power can lead to voltage fluctuations and equipment damage. 3-phase systems allow for a more balanced distribution of loads, preventing these issues and ensuring a stable power supply. Think of it as distributing weight evenly in a truck — it prevents tipping and ensures a smoother ride.
Moreover, 3-phase power is often required for large-scale industrial equipment and machinery. Running these machines on a single-phase system would be impractical and inefficient, if not impossible. The superior performance and reliability of 3-phase power are essential for industries that rely on heavy-duty operations.
The stable and reliable power supply offered by 3-phase systems can also reduce the risk of downtime. Power outages and voltage fluctuations can disrupt operations, leading to lost productivity and revenue. By providing a more consistent power source, 3-phase systems can minimize these disruptions and keep businesses running smoothly.

Why 3Phase Not 4 Or 5 Phase? Electrical Volt
Real-World Applications
4. From Factories to Data Centers
3-phase power is the backbone of many industries. Manufacturing plants rely on it to power heavy machinery, assembly lines, and automated systems. The efficient and reliable power delivery ensures consistent production and minimizes downtime. From stamping presses to robotic welders, 3-phase power keeps these machines humming.
Commercial buildings, such as office towers and shopping malls, also benefit from 3-phase power. It's used to run large HVAC systems, elevators, and other essential equipment. The ability to balance loads and reduce voltage fluctuations is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and safe environment for occupants. Imagine trying to run a skyscraper on single-phase power — it simply wouldn't be feasible.
Data centers, which require a constant and reliable power supply to operate servers and networking equipment, are another major user of 3-phase power. Even a brief power outage can lead to data loss and significant financial losses. 3-phase systems provide the stability and redundancy needed to keep these critical facilities running 24/7.
Even renewable energy systems, such as large-scale solar farms and wind turbines, often utilize 3-phase power to transmit electricity to the grid. The efficient and reliable transmission capabilities of 3-phase systems are essential for integrating these renewable energy sources into the power grid.

Why Is 3 Phase Better Than Single » Wiring Work
Making the Switch
5. Evaluating Your Power Needs
Deciding whether to switch to a 3-phase system depends on your specific power requirements and energy consumption. If you're running a small business with only a few light appliances, single-phase power might be sufficient. However, if you're expanding your operations and adding heavy machinery, 3-phase power could be a worthwhile investment.
Consider your long-term energy costs. While the initial investment in a 3-phase system might be higher, the long-term savings on electricity bills can quickly offset these costs. Conduct a thorough energy audit to assess your current consumption and project future needs. Consult with a qualified electrician to determine the best solution for your situation.
Another factor to consider is the availability of 3-phase power in your area. In some rural areas, 3-phase power may not be readily available, requiring additional infrastructure upgrades. Check with your local utility company to determine the feasibility and cost of connecting to a 3-phase power grid.
Ultimately, the decision to switch to 3-phase power is a strategic one that should be based on a careful analysis of your energy needs, costs, and long-term goals. By understanding the benefits of 3-phase power and evaluating your specific situation, you can make an informed decision that will save you money and improve the efficiency of your operations.

Singlephase (1phase) And Threephase (3phase) Electrical Power
FAQ
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Q: What exactly is 3-phase power?
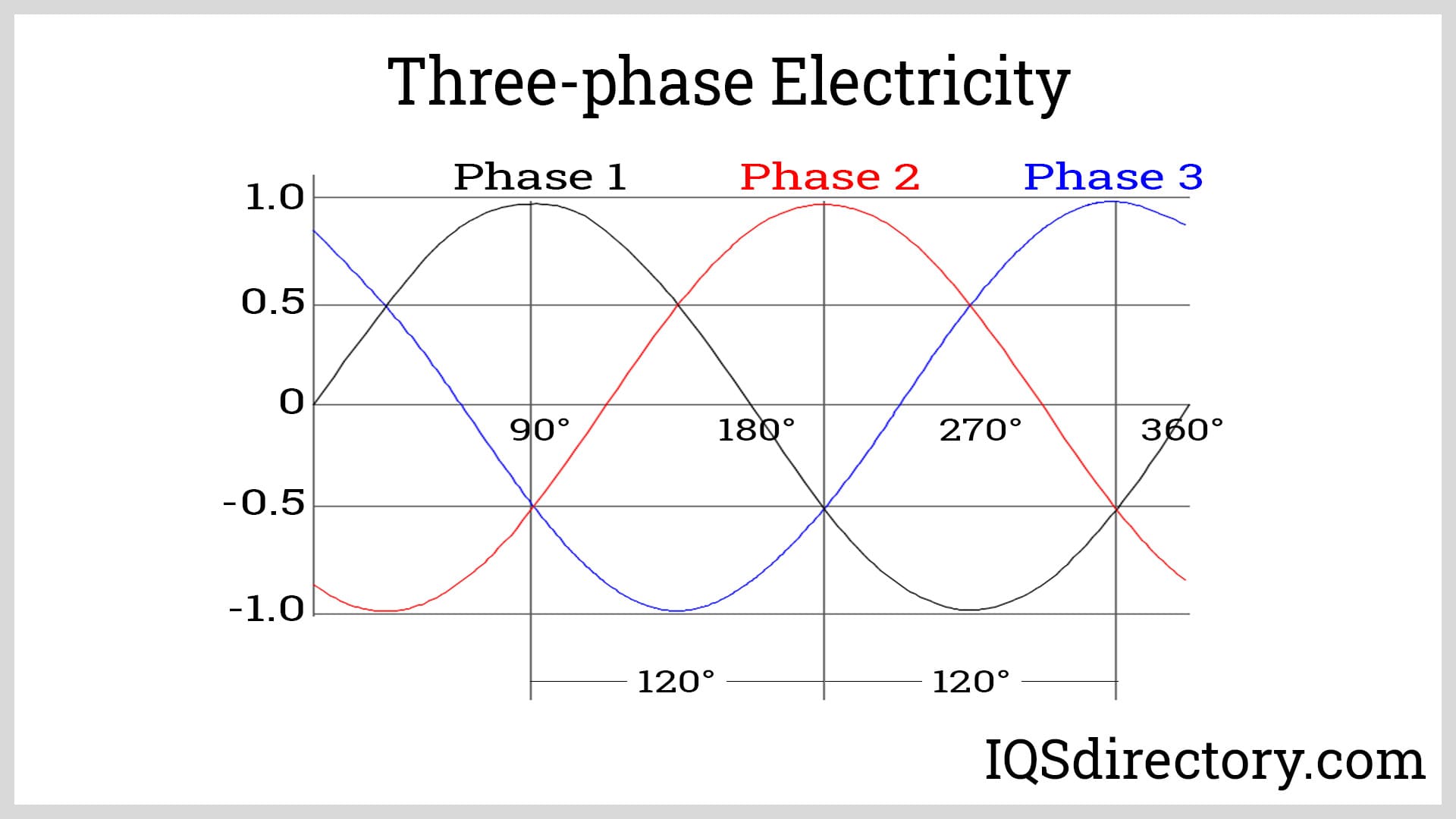
A: Imagine three separate waves of power, all timed perfectly so they never overlap but constantly provide a steady flow. That's 3-phase power in a nutshell — three alternating currents offset by 120 degrees, working together to deliver consistent energy.
Q: Is 3-phase power dangerous?
A: Not inherently more dangerous than single-phase, but it does operate at higher voltages in industrial settings. That's why it's super important to have qualified electricians handling installations and maintenance. Respect for electricity is always key!
Q: Can I use 3-phase power in my home?
A: Probably not necessary (or easily accessible). Most homes run perfectly well on single-phase. 3-phase is typically for businesses and industries with high power demands. Unless you're planning on running a metal forge in your basement, you're likely good with single-phase!
Q: How do I know if I need 3-phase power?
A: If you're running large, power-hungry motors or equipment, and you're noticing flickering lights or tripping breakers, it might be time to consider 3-phase. A qualified electrician can assess your needs and give you a definitive answer. It's always best to consult the professionals!